The Future of Hearing Aid Personalization
Hearing aids have come a long way from the one-size-fits-all approach of
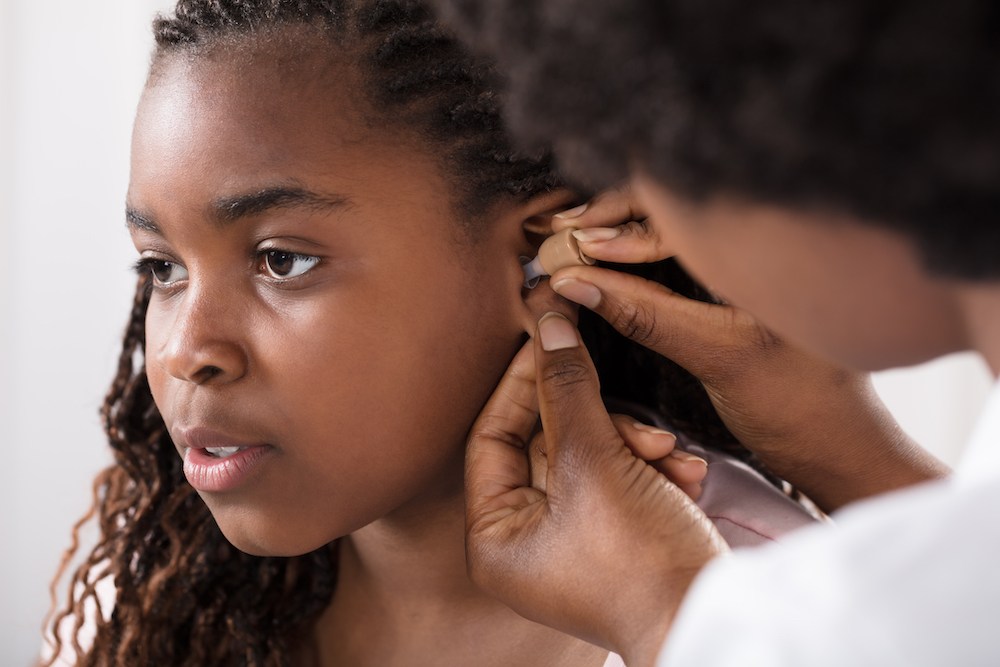


Hearing aids have come a long way from the one-size-fits-all approach of
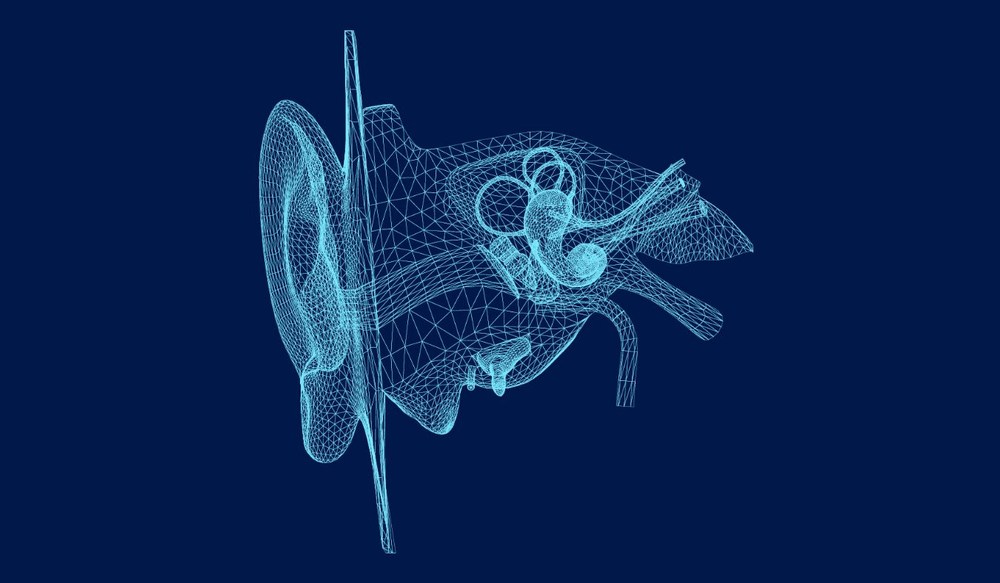
You use your hearing constantly throughout the day, often without

Allergy season brings familiar symptoms like sneezing, watery eyes and